What is data governance?
Data governance refers to the overall management of the availability, usability, integrity and security of data within an organisation. It involves defining and implementing policies, procedures and standards to ensure that data is managed effectively and responsibly throughout its lifecycle. The goal of data governance is to ensure that data is accurate, consistent and reliable and that it meets the needs of the business while complying with relevant regulations.
Data governance may seem like a daunting business process where you’ll be met with endless spreadsheets and red tape. But the reality is it’s a straightforward range of activities that will help you to proactively manage and improve the quality of your business data.
There’s no one-size-fits-all approach when it comes to enterprise data governance, instead the framework must fit your organisation’s structure and practices for it to be beneficial. You need to think about what you currently do with your data and how you want to use it moving forward.
What is master data governance?
Master data governance is a subset of data governance that specifically focuses on the management and oversight of an organisation’s master data. Master data refers to the core business entities and concepts that are used across multiple business processes and applications.
Examples of master data include customer information, product details, employee records and vendor data. Master data is critical for the smooth functioning of various business operations and master data governance aims to ensure its accuracy, consistency and reliability.
What is cloud data governance?
Cloud data governance refers to the policies, processes and controls that organisations put in place to manage and protect their data in cloud environments. With the increasing adoption of cloud-based services, organisations are leveraging the scalability, flexibility and cost-effectiveness offered by cloud platforms. However, ensuring proper governance of data in the cloud is essential to maintain data integrity, security and compliance with regulations.
What are the components of a data governance framework?
The basic components of a data governance framework are policy, processes and roles and responsibilities.
Data governance policy
A data governance policy is a set of documented guidelines, rules and procedures that define how an organisation manages and governs its data assets. This policy serves as a framework for ensuring that data is handled in a consistent, secure and compliant manner across the organisation.
Putting a data governance policy in place that states your company’s data governance intention is the backbone to your framework and data strategy. It outlines how your business views and uses data, as well as the changes you wish to make (and why) and how you plan to manage data moving forward based on your business needs.
What is a data governance maturity model?
A data governance maturity model is a framework that organisations use to access and improve their data governance practices over time. It provides a structured way to evaluate the maturity of an organisation's data governance capabilities and identifies areas for improvement. Maturity models typically have multiple levels or stages, each representing a higher level of maturity and sophistication in data governance.
Data governance processes
Data governance processes are a set of structured activities and workflows designed to implement and maintain the principles and policies outlined in a data governance framework. These processes ensure that data is managed effectively, securely and in compliance with relevant regulations. Your processes and the tasks that arise from each step, can include things like data quality reporting and data quality issue management.
Data governance roles and responsibilities
In order to maintain quality data that’s reliable and accurate, it must be proactively managed. This means planning who in the business will be responsible for each aspect of data governance, including their scope of work and extent of involvement.
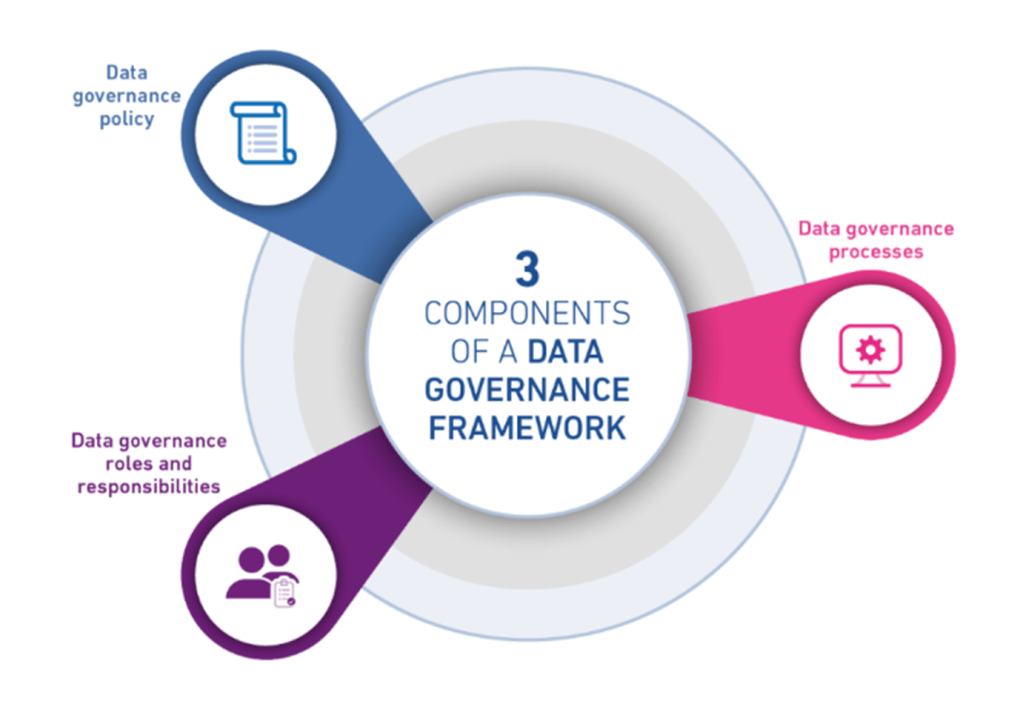
It’s worth remembering that each element of the framework is essential for a best practice strategy, as they all work alongside one another. Having an established data governance policy and roles is good, but if there’s no process and guidelines in place your results will be inconsistent. Similarly, if you have a process and policy but no roles, there will be no ownership of the governance making it harder for action to take place.
What is the difference between data quality and data governance?
While on the surface it may seem like the same thing, the truth is data quality and data governance are separate principles that work together – and you shouldn’t have one without the other.
Data quality describes what kind of shape your data is in by looking at its accuracy, completeness, relevance and whether it is fit for purpose.
Data governance describes what you do to keep your data in shape by looking at how you manage its reliability, security, availability, and usability.
Both rely on each other if your business is to continually – and successfully – use data in a meaningful way. Often businesses put a lot of hard work into improving the quality of their data, but don’t have a robust governance strategy in place to ensure it remains up to date and relevant. This in turn means any positive benefits that the data provides when it comes to business decisions, are short lived.
Why is data governance important?
If you’ve spent time cleaning up your bad data to ensure it’s high quality and organised, you’ll already know what kind of benefits are to be had. However, putting a data governance framework in place to manage that data is like turbocharging its effectiveness.
From better analytics which lead to better decision making, to a reduction in errors and integrity, here are some of the key benefits:
The quality of your data is improved
By putting a proactively managed data governance structure in place, you’ll reap the rewards of more organised and insightful data. By ensuring everything has been captured correctly and is up to date, you can spot any gaps you may need to fill, you can maintain the quality of your data and create a database that you’re confident in.
Data becomes easier to access and manage
The more your business grows, the more you’re likely to increase your data assets, sources and volumes. More data may seem good on the surface, but if it’s unruly and without rationale it can be difficult to get any meaning or value from it. A data governance framework will help you to categorise, find, understand and use the data assets effectively.
Complying with regulations becomes easier
Whatever the industry, if you store customer data you’re likely required to comply with lots of regulations. Having the processes, policy and roles of data governance in place will help make compliance easier, clearer, demonstrable and more efficient.
You can make better business decisions
By having a clear and accurate idea of all the data your business has, you can make better informed and more trusted business decisions that can lead to:
- Increased revenue
- Reduced operational costs
- Reduced risk
- Improved customer satisfaction and retention

What are the roles and responsibilities within data governance?
Data governance doesn’t just fall on one person’s shoulders to strategise, implement, and manage. It’s great to have a champion of the business process, but the truth is data touches every role and you’ll need the whole organisation to get involved in order for your governance to be a success.
From operational workers to senior management, everyone will fit into one of these four categories:
Data owner – someone who is accountable for the overall strategy, quality and guidance of a dataset.
Data steward – someone who is responsible for a dataset on a day-to-day basis and implements governance policies and monitoring compliance.
Data producer – someone who creates or captures the data, as well as tracking metrics and fixing any errors.
Data consumer – someone who uses the data in their day-to-day job.
How do I get started with data governance?
Many businesses say that they struggle to implement a data governance process, but getting started and maintaining your framework doesn’t have to be overwhelming.
- Identify your data – The first step is to identify the data you have and where it’s held. Without a clear understanding of the data and its whereabouts, effective data governance becomes challenging.
- Get the data organised – A meaningful data governance process requires quality enterprise data, so it’s essential to get everything complete, accurate and cleansed.
- Bring a team together – A data governance program will need dedicated staff from all areas of the business to help lay the foundations for a useful and sustainable framework. Include data owners from various departments, including marketing, finance and compliance, as this diverse expertise will help define the vision, goals and success metrics to capture.
- Set up the processes – Now that you’ve found the right people, together you can set up processes that address data security, monitoring, observation and reporting. Consider your plan for accountability, requirements, issue resolution and analysis to support data acquisition, compliance, financial priorities and how to drive improvement initiatives.
- Share the insights – Once you’ve extracted insights and trends from your data through data analytics, be sure to think about how you’ll communicate any learnings and recommendations from your data governance strategy to the wider business, so they can implement the insights into their own areas.
How can we help?
If you’re ready to implement a data governance framework, our expert data consultants and data governance tools can help you every step of the way.
Firstly, you’ll want to get your enterprise data in shape and that’s where our range of data quality and analytics tools can help.
Then, Experian Aperture Data Governance should be your next port of call. Designed for data governance leaders, our next-generation data management technology gives you the control and high standards needed for a robust data governance process.
Aperture Data Governance provides an easy-to-use, ‘out of the box’ solution that will provide governance workflows, stakeholder reporting, data stewardship monitoring and data quality rules you can set to satisfy regulators.
